
What Credit Score Do Home Buyers Need to Buy a House in 2025? What Credit Score Do Home Buyers Need to Buy a House in 2025?
When you're looking to buy a home, there are many factors that lenders take into account when determining whether you qualify for a mortgage but one of the most significant is your credit score.
Quick Links:
- What is a Credit Score?
- What are the Credit Score Ranges?
- What is a Tri-Merge Credit Report and Why Is It Important for Home Buyers?
- What Factors Impact Your Credit Score?
- What Factors Don't Impact Your Credit Score?
- What Credit Score Do You Need to Buy a House?
- Does Your Credit Score Impact What Type of Mortgage Loan You Qualify For?
- How Can You Increase Your Credit Score Before You Apply for a Mortgage?
- How Can You Review Your Credit History?
Lenders use credit score to evaluate prospective home buyers ability to make mortgage payments on time, and a buyer's credit score and credit history can impact what loan terms or interest rate they qualify for. It goes without saying that it's important to know where your credit score stands when you're buying a house.
Below you'll learn what credit score evaluates, the different types of credit score, generally what is considered a good credit score and bad credit score, how you can improve your credit score when you're looking to buy a home, and more!
- Credit score is represented by a number between 300 and 850.
- The higher credit score you have, the better you look to mortgage lenders when you’re buying a house.
- Every lender evaluates credit score differently
- There is no universal minimum credit score required to buy a house
- Lenders use a Tri-Merge Credit report to collate your credit information from the three major credit bureaus: Equifax, Experian, and Transunion.
- Credit score is influenced by factors including paying your bills on time and how much of your available credit you use.
What is a Credit Score?
A credit score is represented by a three-digit number, usually between 300 and 850, and indicates how likely you are to pay your bills and repay money that has been borrowed. The higher credit score you have, the better you look to lenders when you're looking to buy a home. On the other hand, a lower credit score means you may have trouble qualifying for certain types of loans.
Your credit score is calculated by credit bureaus like Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion who gather information about your credit accounts and compile them into your credit report. These companies use a variety of factors to calculate your credit score including the number of open accounts you have, your total debt, how timely you are paying your bills, and existing loan repayment history.
There are two companies that predominantly generate credit scores, and you've probably heard of the first one -- the Fair Isaac Corporation, or FICO. The other most common credit score you'll see is VantageScore. Both companies evaluate credit score on a scale of 300 to 850, and while they use the same data to generate scores they weigh your information differently so don't be surprised if you check your score in two different places and see a slightly different number.
What are the Credit Score Ranges?
Every lender and creditor will have their own standards for how they evaluate your credit score, but generally, credit scores can be classified with the following guidelines:
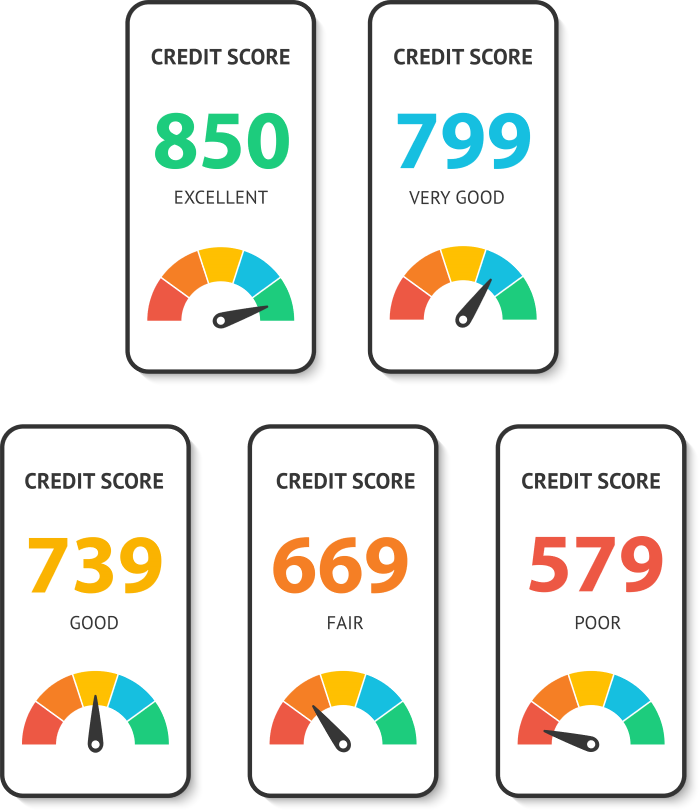
- 800-850: Excellent
- 740-799: Very Good
- 670-739: Good
- 580-669: Fair
- 579 or Lower: Poor
The highest score possible is 850, but a perfect score is hard to achieve. Because every lender evaluates credit differently, there is no hard and fast rule for what score will get you approved for a particular interest rate or loan product when you're looking for a home. A higher score generally suggests that you have shown responsible financial behavior in the past and indicates to lenders and creditors that they can be confident that you will be able to make your monthly mortgage payment without issue.
What is a Tri-Merge Credit Report and Why Is It Important for Home Buyers?
If you're looking for a home and applying for a mortgage, you'll need a Tri-Merge Credit Report. Also known as a Residential Mortgage Credit Report, a Tri-Merge report is usually pulled by your lender and contains your credit report from the three major credit bureaus mentioned above (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion), and merges data from all three into a single, comprehensive document for lenders to evaluate.
So why do mortgage lenders use Tri-Merge reports? The three major credit bureaus do not share their data with one another, and Tri-Merge reports are generated by intermediary bureaus that specialize in merging credit report data from each credit bureau along with the mortgage applicant's and co-applicant's FICO score.
Lenders use Tri-Merge reports to ensure you don't have any notable credit issues such as past-due accounts, unpaid debt, high balances on existing credit accounts, newly-opened accounts, or too many recent credit inquiries. Any of these will be red flags to mortgage lenders when they are considering whether to approve you for a mortgage.
What Factors Impact Your Credit Score?
As mentioned above, there are many things that can impact your credit score both positively and negatively. The two things that both FICO and VantageScore value the most are whether you pay your bills on time and how much of your available credit you actually use.
It may seem like a small thing, but making sure you pay your bills on time has a huge impact on your credit score -- late payments and especially any payments that are more than 30 days past due can negatively impact your credit score for years. Similarly, credit utilization or how much of your existing credit limit you use as weighed heavily by both FICO and Vantage Score. Generally, it's best practice to use less than 30% of your credit limit but the lower the percentage the better when you're applying for a home loan.
Other factors that, while less impactful, can still influence your credit score include your credit age (the longer you've had a credit account the better for your score), your credit mix (your score will be better if you have more than one type of credit), and how recently you've applied for credit (a recent inquiry may result in a temporary deduction on your score).
What Factors Don't Impact Your Credit Score?
There are plenty of misconceptions out there about what can and can't move the needle of your credit score. Demographic characteristics like race, ethnicity, gender, marital status, and age are not part of credit score calculations. Employment history including salary, title, and employer, is also not factored into your credit score. Where you currently reside is not factored into your report.
What Credit Score Do You Need to Buy a House?
It goes without saying that one of the most common questions first-time homebuyers have about the homebuying and mortgage process is what is the minimum credit score needed to buy a home? The answer may not be as straightforward as you think.
Every lender evaluates credit scores differently, and as mentioned above there is no universal credit score requirement that homebuyers must meet during the mortgage process. Generally, a high credit score improves your chances of being approved for a mortgage loan while a low credit score may hinder your ability to buy a home. Some lenders may even offer a lower interest rate if you have a higher credit score.
Does Your Credit Score Impact What Type of Mortgage Loan You Qualify For?
While there is no universal minimum credit score to buy a house your credit score may impact what type of loan program or mortgage rate you can qualify for, and while credit score minimums for different loan programs will vary by lender it's important to learn generally what credit score you need for different types of mortgage loans.
For instance, conventional loans generally require a higher credit score to qualify. However even if your credit score isn't high enough for a conventional loan there are some loan products that generally allow for lower credit, such as an FHA loan. An FHA loan will generally have more accommodating credit requirements for borrowers with lower credit scores, although it's important to note that lenders will have their own credit requirements to qualify for an FHA loan. While VA loans don't require a minimum credit score (the main requirement is that you be a veteran, active-duty military member, or an eligible spouse), every VA lender set minimum credit score requirements. To be approved for a Jumbo loan, or a loan that's larger than the conforming loan limit, most lenders will want borrowers with a credit score on the higher end and a solid financial background.
How Can You Increase Your Credit Score Before You Apply for a Mortgage?
So with all this being said what steps can you take to boost your credit score if you're looking to apply for a mortgage loan? It can be overwhelming if you're a first-time home buyer and your credit score isn't where you want it to be, but the good news is that most of the ways to increase your credit score are fairly straightforward and can be enacted immediately.
- Pay your bills on time.
- Use 30% or less of your credit limit.
- Ask for a higher credit limit.
- Keep older credit cards open to maintain a longer average account age.
- Avoid applying for credit -- too many applications in a tight timeframe will negatively impact your score.
- Make credit card payments multiple times per month.
- Dispute errors on your credit report.
How Can You Review Your Credit History?
If you're planning to buy a house and are working toward having good or excellent credit with some of the steps outlined above, it's important to know where you currently stand. The first place to start is with your credit card company. Most credit cards now offer a free credit score as part of your account which is a great resource to use as you're looking to qualify for a mortgage loan. Wherever you check your credit score be sure to use the same source every time you check. As noted above, different sources calculate credit score differently so checking your score in different places may generate different results.



